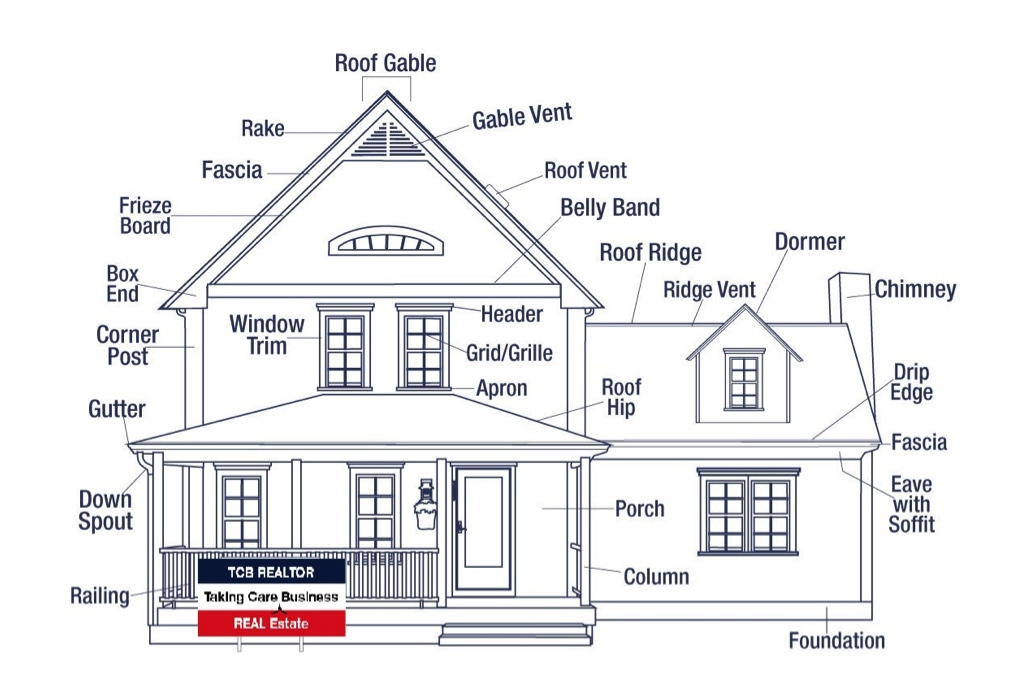
Above is an example of a traditional style exterior. There are many different styles of homes, which may or may not contain the labeled parts.
The Roof:
- Gable – The triangular part of a wall where roof pitches meets and come to a peak.
- Ridge – The top peak of a gable roof running horizontally where two sloping sides meet.
- Hip – A downward sloping junction of the roof where sloping sides meet. This occurs on pitched roofs with sloping planes that join along their sides, like the edges of a pyramid.
- Rake – The rake is the outer slanting edge of a gable roof end that runs from the ridge to the eave.
- Drip Edge – A metal strip edge extending beyond the roof that directs water outward and prevents water from curling back over the shingles.
- Fascia – Decorative & protective horizontal board covering the rafter’s area below the roof edge. Often holds the gutters.
- Eave – The overhanging area of the roof that extends beyond the house to keep rain water away from the lower part of the home.
- Soffit – Covering for the underside of the eave, often vented.
- Box End – The end cap to finish off the soffit and fascia at the gable wall.
Roof Vents:
Roofs need ventilation to exhaust heat from the attic, which can become over-heated if it can’t escape. These vents also help to normalize the attic temperature in cold weather, which prevents condensation and moisture damage. Roof ventilation helps to improve energy efficiency and the home’s life span. There are many different types of roof vents that come in various shapes and sizes.
Gable Vent – A vent located in the gable area of the wall.
Roof Vent – This type of vent is located on the roof itself.
Ridge Vent – This vent is placed along the roof ridge, which is the peak of the roof that runs horizontally. This vent is at the highest point of the roof, which is helpful because heat rises and exhausts passively. You may also see a similar type of vent called a hip vent, which runs along the hip of the roof.
Gutter System
Gutter – These catch the water dripping from the roof and carry it away from the home.
Down Spout – The downward tubing to direct the water down and out from the gutters.
Edges and Ends
Frieze Board – Trim board at the top of the finished wall under the roof’s edge.
Corner Post – The outer corner trim to seal off siding and wall edges.
Foundation – The structural base that the home sits on, normally concrete.
Windows & Doors
Trim – Decorative board around the edges of windows and doors.
Header – Larger decorative trim boards and moldings above windows and doors.
Grid/Grille – Thin inner window trim that visually divides glass. Some are strictly decorative and some also provide structural and stability benefits. They come in many different patterns. Grids are normally rectangular. Grilles often refer to more elaborate patterns. Spelling is seen interchangeably as grille and grill.
Apron – Larger decorative trim boards and moldings below windows.
Specialty Areas
Dormer – An extra wall area that extends out from the roof plane often containing a window.
Chimney – The large protective ventilation area for smoke normally from a fireplace .
Porch – An open front extension around the entrance of the home, normally covered.
Column – Vertical posts which hold up roof extensions, often covered with decorative features.
Railing – Fencing or barrier with small posts, rails, often around an open part of the house like a deck or porch

